Scabies Transmits Person To Person Through Close Skin Contact :Skin Specialist
Sumaira FH Published May 15, 2024 | 10:36 PM

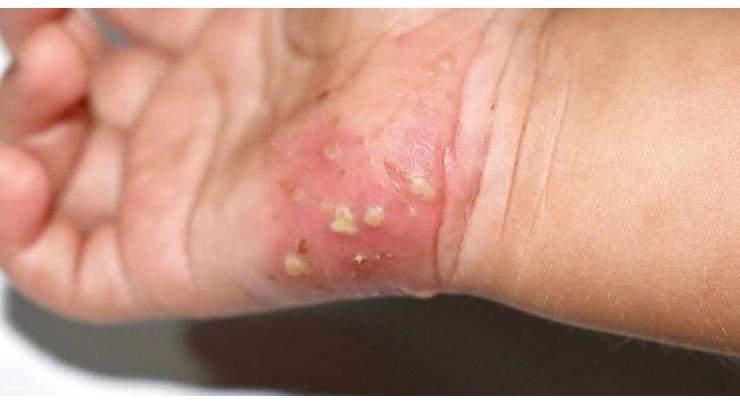
Scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs, causing intense itching and a rash. Scabies can lead to skin sores and serious complications like septicaemia (a bloodstream infection), heart disease and kidney problems
HYDERABAD, (UrduPoint / Pakistan Point News - 15th May, 2024) Scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs, causing intense itching and a rash. Scabies can lead to skin sores and serious complications like septicaemia (a bloodstream infection), heart disease and kidney problems.
Dermatologist / Skin specialist Dr Rajendar Dhirani expressed these views while talking to APP here on Wednesday.
He informed that Scabies spreads easily from person to person, especially among people who live close together. Children and older people in resource-poor areas are at higher risk. Scabies is found in every country but is particularly common in many resource-poor tropical settings, particularly in children and older people. Prevalence among children in these settings may vary from 5% up to 50%. Recurrent infestations are common,he added.
He said that Scabies is transmitted person-to-person through close skin contact (e.g. living in the same residence) with an infested individual. The risk of transmission increases with the level of infestation, with highest risk due to contact with individuals with crusted scabies. Transmission due to contact with infested personal items (e.g., clothes and bed linens) is unlikely with common scabies but may be important for individuals with crusted scabies. As there is an asymptomatic period of infestation, transmission may occur before the initially infested person develops symptoms
To a question about the symptoms he said that it include severe itch, often worse at night;itchy lines (linear burrows) and bumps (papules) on the fingers, wrists, arms, legs and belt area; larger rash in infants and small children, including on the palms, soles of the feet, ankles and scalp.
About the precaution he said that avoid skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, especially if they have an itchy rash; treat all members of the household if someone has scabies to prevent the mites from spreading to others; wash and dry bedding and clothing that has been in contact with the infested person, using hot water and drying in direct sunlight, a hot dryer cycle or dry cleaning; seal items that can’t be washed in a plastic bag for a week to help eliminate the mites; and clean and vacuum or sweep rooms after an infected person has been treated, especially for people with crusted scabies.
He said that Scabies can be treated with topical creams or oral medication in more severe cases. Itchiness often gets worse for 1–2 weeks after treatment starts. Ivermectin taken orally is also highly effective, but it should not be taken by pregnant women or children who weigh less than 15 kg.
Treatments do not kill the parasite’s eggs, and treatment should be repeated to kill newly hatched mites. People do not experience symptoms in the early stages of infestation. To reduce spread, all people in the household should be treated, even if they do not have symptoms.
Other treatments may be needed to treat the complications of scabies. Antiseptics or antibiotics are used to treat bacterial skin infections or impetigo.
Recent Stories

SCN raises voice for halting massive deforestation in KP

IHC seeks date to hold local body elections in Islamabad

UN rights chief slams Israel over deaths of 500 Palestinians in occupied West Ba ..

India tried to kill its most wanted man on Canadian soil too, report reveals

South Punjab lawyers call for video-link hearing facility in Multan

Police claim to arrest four persons with bike, weapons, cell phone

PTI near to cross limits: Tariq Fazal

ICCI President greets newly-elected body of APP Employees Union

FBR unearths network of tax fraudsters

18 gamblers, held during a raid at two gambling dens

ECP seeks ET records on PML-N MNAs' petition

AJK environment minister seeks collective role of society to successfully meet f ..
More Stories From Health
-

Healthy lifestyle imperative for diabetes control: experts
5 hours ago -

ATH admin seals drug-resistant TB center
9 hours ago -

Outbreak alert: 25 minors hospitalized with measles at THQ Burewala
1 day ago -

Polio eradication from country top priority: ADC
3 days ago -

PHC directs hospitals to prepare for measles, heat stroke patients
4 days ago -

Harmful effects of smoking highlighted
4 days ago
-

Pineapple---a best source to fight heatstroke
5 days ago -

13 children contracted measles in two days in Burewala
5 days ago -

CM aide lauded timely respond of District administration to tackle Congo virus
6 days ago -

DC Kohat urges parents to vaccinate children against polio to prevent disability
6 days ago -

Health authority advises preventive measures to avoid the Congo virus
6 days ago -

UHS bars medical colleges from Imposing fines on students
7 days ago











